Selected Publications
Research works are under review of top-notch prestigious journals (impact factor > xx) that are forthcoming. Research works have been published at Nature Medicine, PNAS, RAL, ICRA, IROS, RoboSoft, etc.
Wireless multimodal wearable sensors with XAI (high-impact first-authored papers forthcoming)
- Key words: Digital health, multimodality, disease diagnosis, cardiovascular health, neurology, drug delivery, behavior science
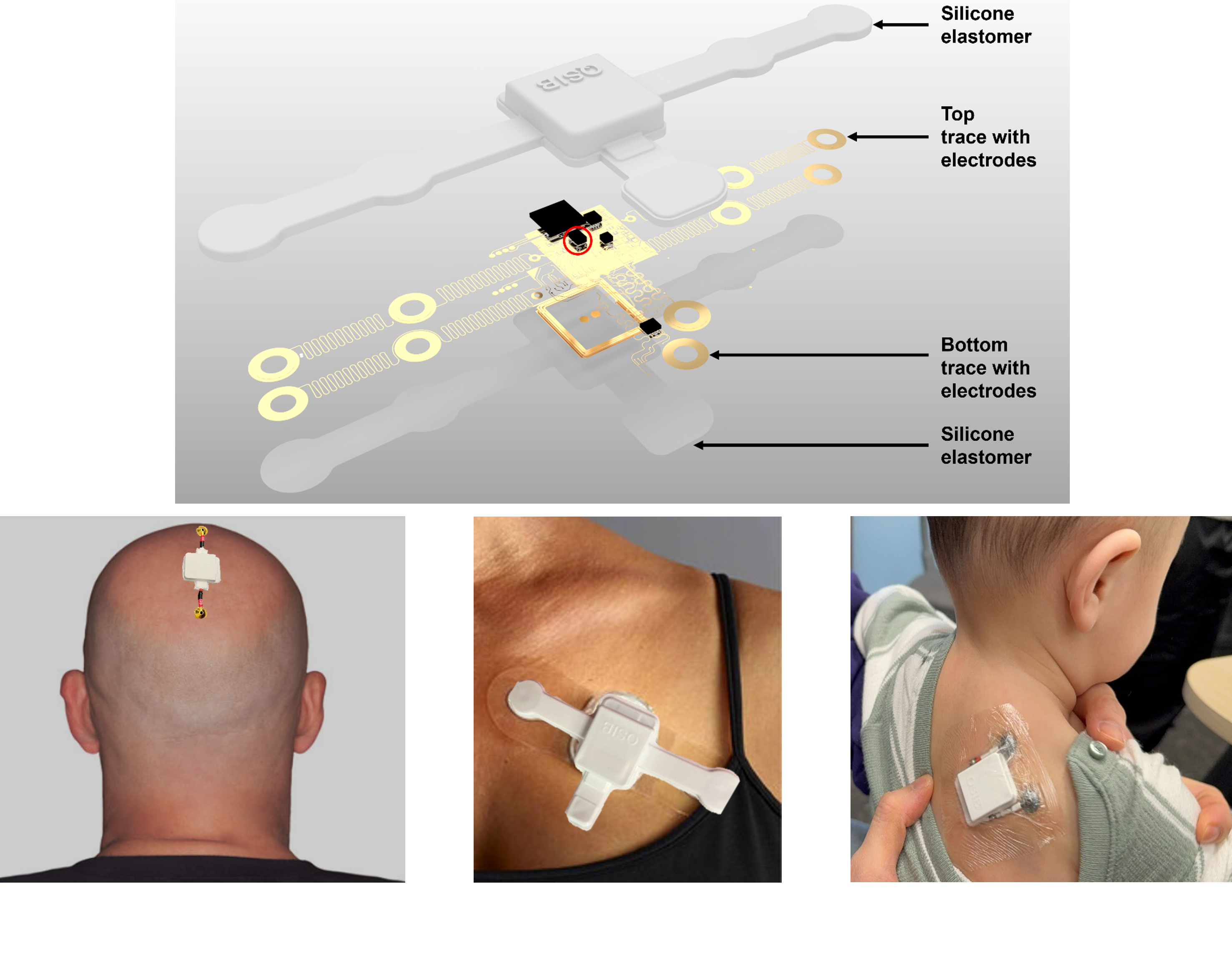
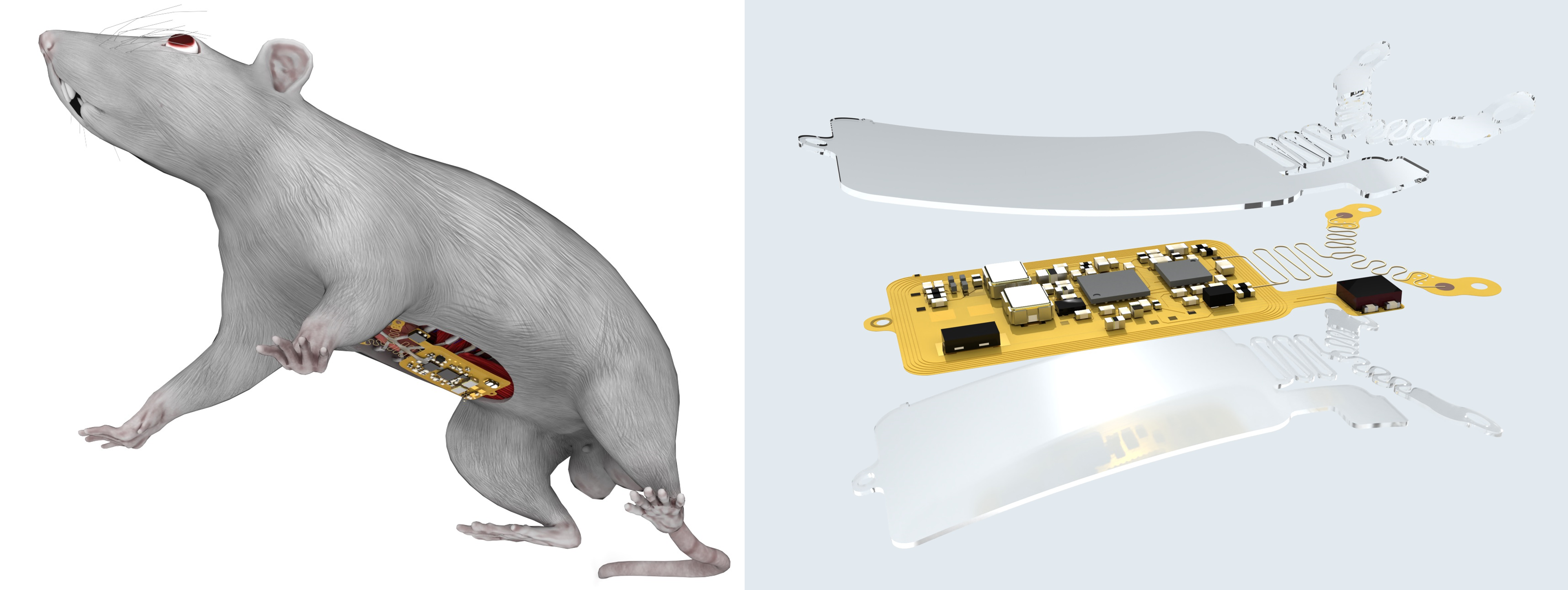
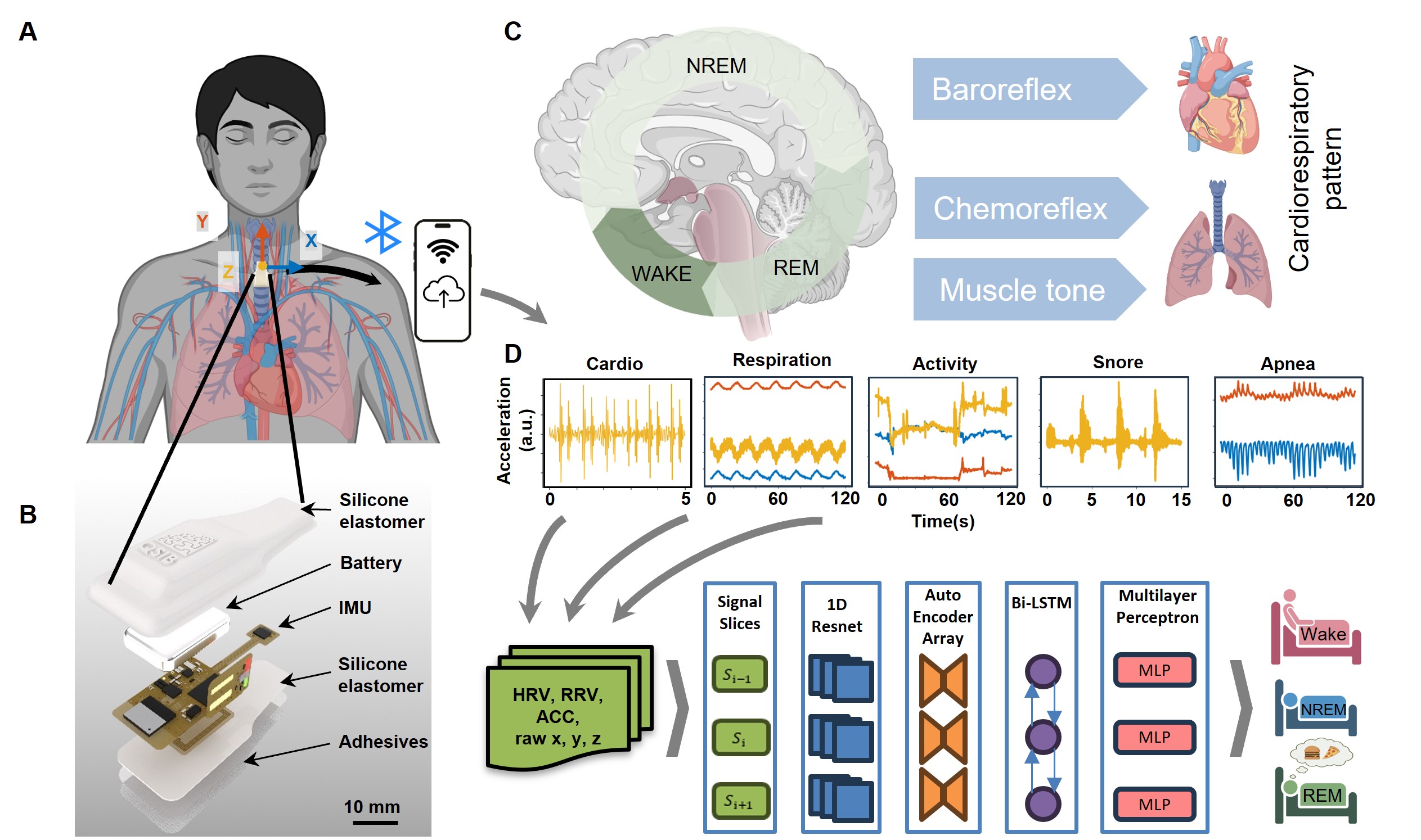
- Y. Du#, J. Gu#, S. Duan#, J. Trueb, A. Tzavelis, H.-S. Shin, H. Arafa, X. Li, Y. Huang, A. N. Carr, C. R. Davies, J. A. Rogers, A skin-interfaced wireless wearable device and data analytics approach for sleep-stage and disorder detection,
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), 2025, Media coverage 1, Media coverage 2
Key words: Wearable electronics, digital health, sleep study, sleep apneas, data analytics
- L. C. Alarcón-Segovia, K. E. Madsen, C. Liu, S. H. Kim, T. W. Park, Y. Du, K. Salame, J. Rogers,
Ultralow-cost hydrogel electrolytes based on agricultural by-products for distributed electrophysiological recording in resource-limited settings, ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, April 2025
Pain study with multimodal wearables in the NICU
- Slattery, S., Pessano, S., Yoo, Du, Y., J., Oh, S., Jeong, H., Alla, A., Rand, C., Hamvas, A., Mayer, D., Rogers, J., Continuous monitoring with wireless sensors and applied diagnostics for pain with Clinical Sensor Pain Scale and computer-aided Automated Sensor Pain Scale in the NICU, BMJ Health & Care Informatics (Under review)
Autonomous agricultural robots
- Du, Y., Saha, S.*, Sandha, S., Lovekin, A.#, Wu, J., Siddharth, S.,Chowdhary, M., Jawed, M. K.,Srivastava, M., Neural-Kalman GNSS/INS Navigation for Precision Agriculture, ICRA, 2023 Link
Precision agricultural robots require high-resolution navigation solutions. In this paper, we introduce a robust neural-inertial sequence learning approach to track such robots with ultra-intermittent GNSS updates. First, we propose an ultra-lightweight neural-Kalman filter that can track agricultural robots within 1.4 m (1.4–5.8× better than competing techniques), while tracking within 2.75 m with 20 mins of GPS outage. Second, we introduce a user-friendly video-processing toolbox to generate high-resolution (±5 cm) position data for fine-tuning pre-trained neural-inertial models in the field. Third, we introduce the first and largest (6.5 hours, 4.5 km, 3 phases) public neural-inertial navigation dataset for precision agricultural robots. The dataset, toolbox, and code are available at: https://github.com/nesl/agrobot.
- Du, Y., Zhang, G.#, Tsang D.#, Jawed, M. K., Deep-CNN based real-time robotic multi-class weed identification, IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2022 Link
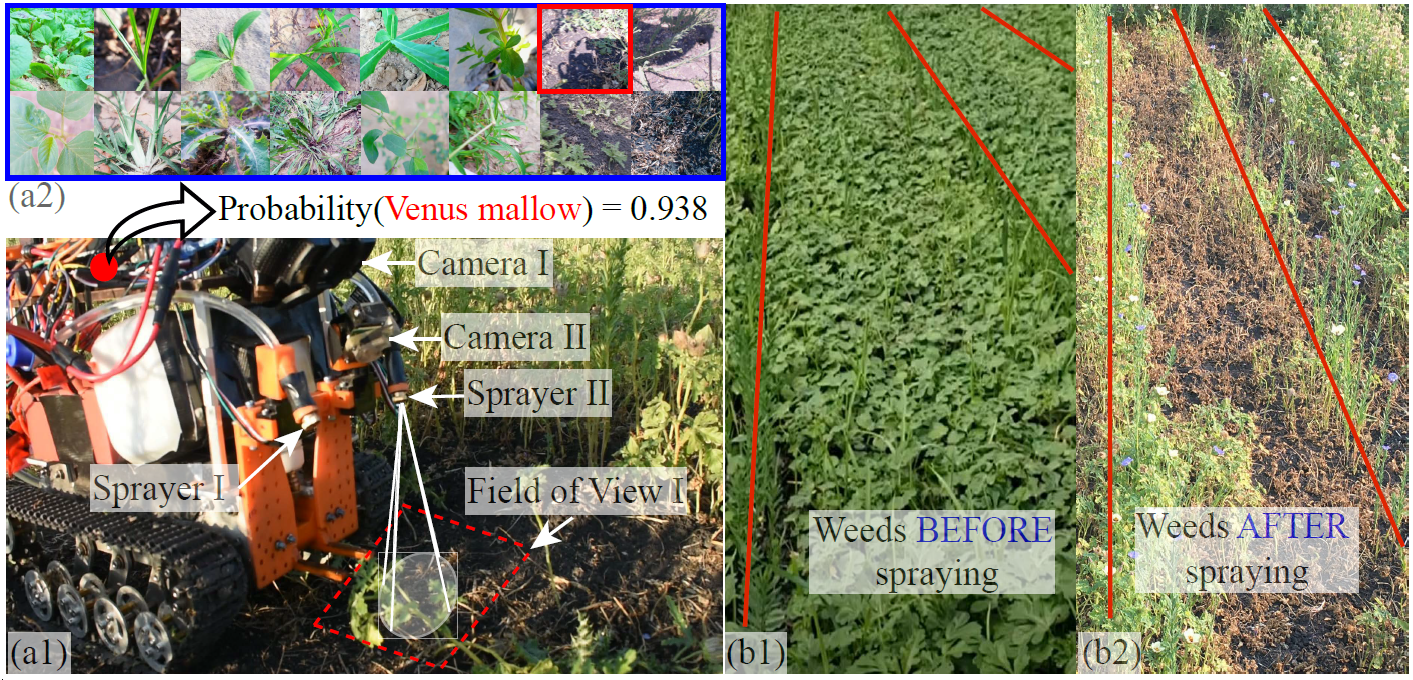
Smart weeding systems to perform plant-specific operations can contribute to the sustainability of agriculture and the environment. Despite monumental advances in autonomous robotic technologies for precision weed management in recent years, work on under-canopy weeding in fields is yet to be realized. A prerequisite of such systems is reliable detection and classification of weeds to avoid mistakenly spraying and, thus, damaging the surrounding plants. Real-time multi-class weed identification enables species-specific treatment of weeds and significantly reduces the amount of herbicide use. Here, our first contribution is the first adequately large realistic image dataset AIWeeds (one/multiple kinds of weeds in one image), a library of about 10,000 annotated images of flax and the 14 most common weeds in fields and gardens taken from 20 different locations in North Dakota, California, and Central China. Second, we provide a full pipeline from model training with maximum efficiency to deploying the TensorRT-optimized model onto a single board computer. Based on AIWeeds and the pipeline, we present a baseline for classification performance using five benchmark CNN models. Among them, MobileNetV2, with both the shortest inference time and lowest memory consumption, is the qualified candidate for real-time applications. Finally, we deploy MobileNetV2 onto our own compact autonomous robot SAMBot for real-time weed detection. The 90% test accuracy realized in previously unseen scenes in flax fields (with a row spacing of 0.2-0.3 m), with crops and weeds, distortion, blur, and shadows, is a milestone towards precision weed control in the real world. We have publicly released the dataset and code to generate the results at https://github.com/StructuresComp/Multi-class-Weed-Classification.
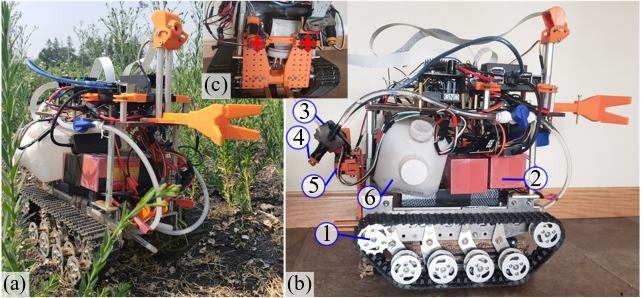
- Du, Y., Mallajosyula, B.#, Sun, D.#, Chen, J.#, Zhao, Z.#, Rahman, M., Quadir, M., Jawed, M. K., A Low-cost Robot with Autonomous Recharge and Navigation for Weed Control in Fields with Narrow Row Spacing, International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Prague, Czech Republic, 2021 (Finalists for Best Paper Award on Agri-Robotics, Best Paper Award on Robot Mechanisms and Design)
Modern herbicide application in agricultural settings typically relies on either large scale sprayers that dispense herbicide over crops and weeds alike or portable sprayers that require labor intensive manual operation. The former method results in overuse of herbicide and reduction in crop yield while the latter is often untenable in large scale operations. This paper presents the first fully autonomous robot for weed management for row crops capable of computer vision based navigation, weed detection, complete field coverage, and automatic recharge for under $400. The target application is autonomous interrow weed control in crop fields, e.g. flax and canola, where the spacing between croplines is as small as one foot. The proposed robot is small enough to pass between croplines at all stages of plant growth while detecting weeds and spraying herbicide. A recharging system incorporates newly designed robotic hardware, a ramp, a robotic charging arm, and a mobile charging station. An integrated vision algorithm is employed to assist with charger alignment effectively. Combined, they enable the robot to work continuously in the field without access to electricity. In addition, a color-based contour algorithm combined with preprocessing techniques is applied for robust navigation relying on the input from the onboard monocular camera. Incorporating such compact robots into farms could help automate weed control, even during late stages of growth, and reduce herbicide use by targeting weeds with precision. The robotic platform is field-tested in the flaxseed fields of North Dakota.
Edge AI-related healthcare & inertial navigation
- Forthcoming several wearable and implantable sensors with deployable AI algorithms with limited computational power and memory
- Saha, S., Du, Y., Sandha, S., Garcia, L., Jawed, M. K.,Srivastava, M., Inertial Navigation on Extremely Resource-Constrained Platforms: Methods, Opportunities and Challenges, IEEE/ION PLANS, 2023 link
Robotic arm control for autonomous robotic painting
- Du, Y., Deng, Z. #, Fang, Z.#, Wang, Y.#, Nagata, T.#, Bansal, K., Quadir, M., Jawed, M. K., Vision and force based autonomous coating with rollers, IROS, Las Vegas, NV, USA, pp. 9954-9960, 202 Link
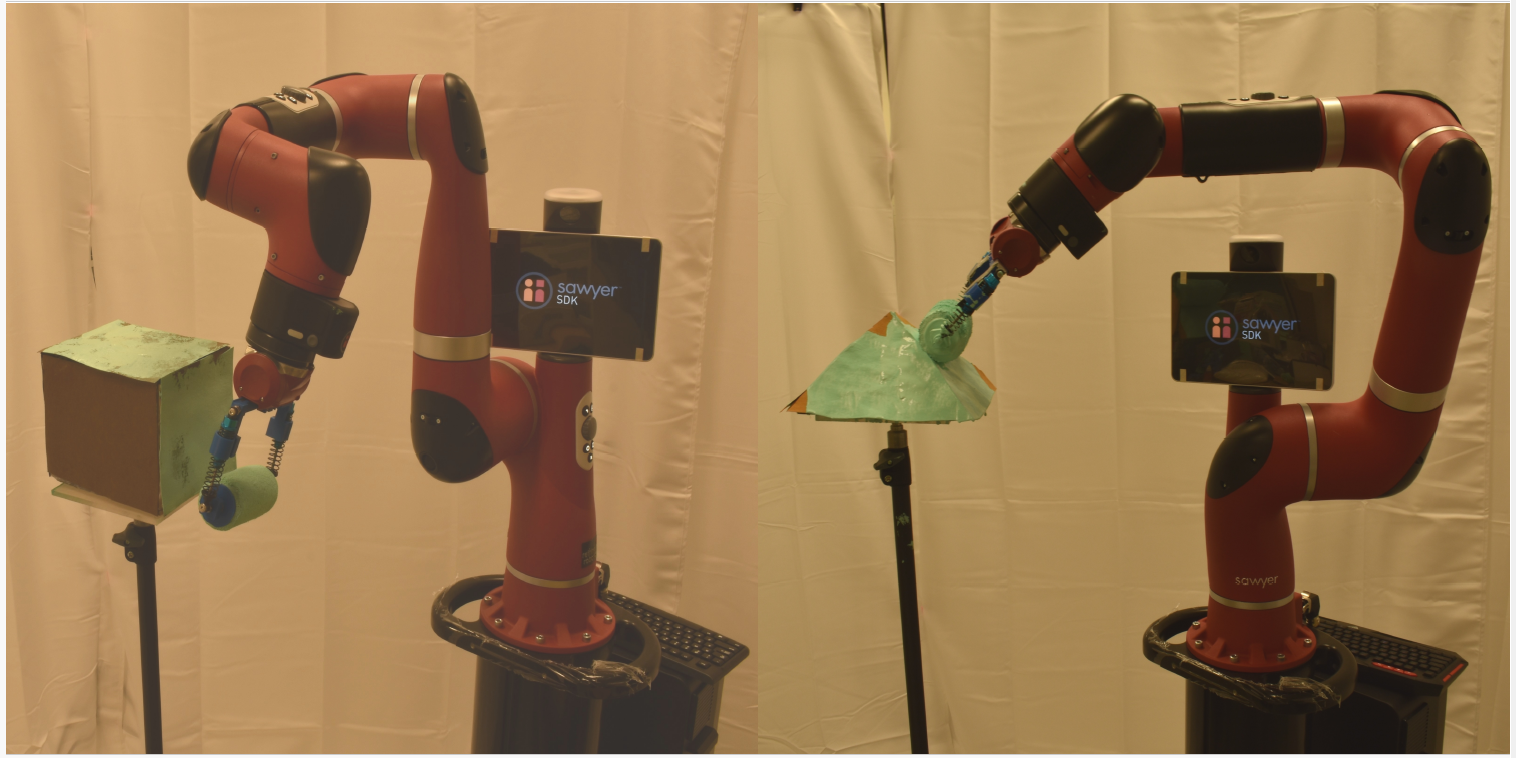
- Du, Y., Bansal, K., Palan, E., Quadir, M., Jawed, M. K., Robotic Painting: Mimicking Human Applicators, Journal of Coatings Technology and Research 2022 link
Bacteria-inspired flagellated robots
- Du, Y., Lam, J.,#, Sachanandani, K.#, Jawed, M. K., Modeling the locomotion of articulated soft robots in granular medium, IEEE Robotics and Automation Letter (RAL) 2022 & ICRA 2023 link
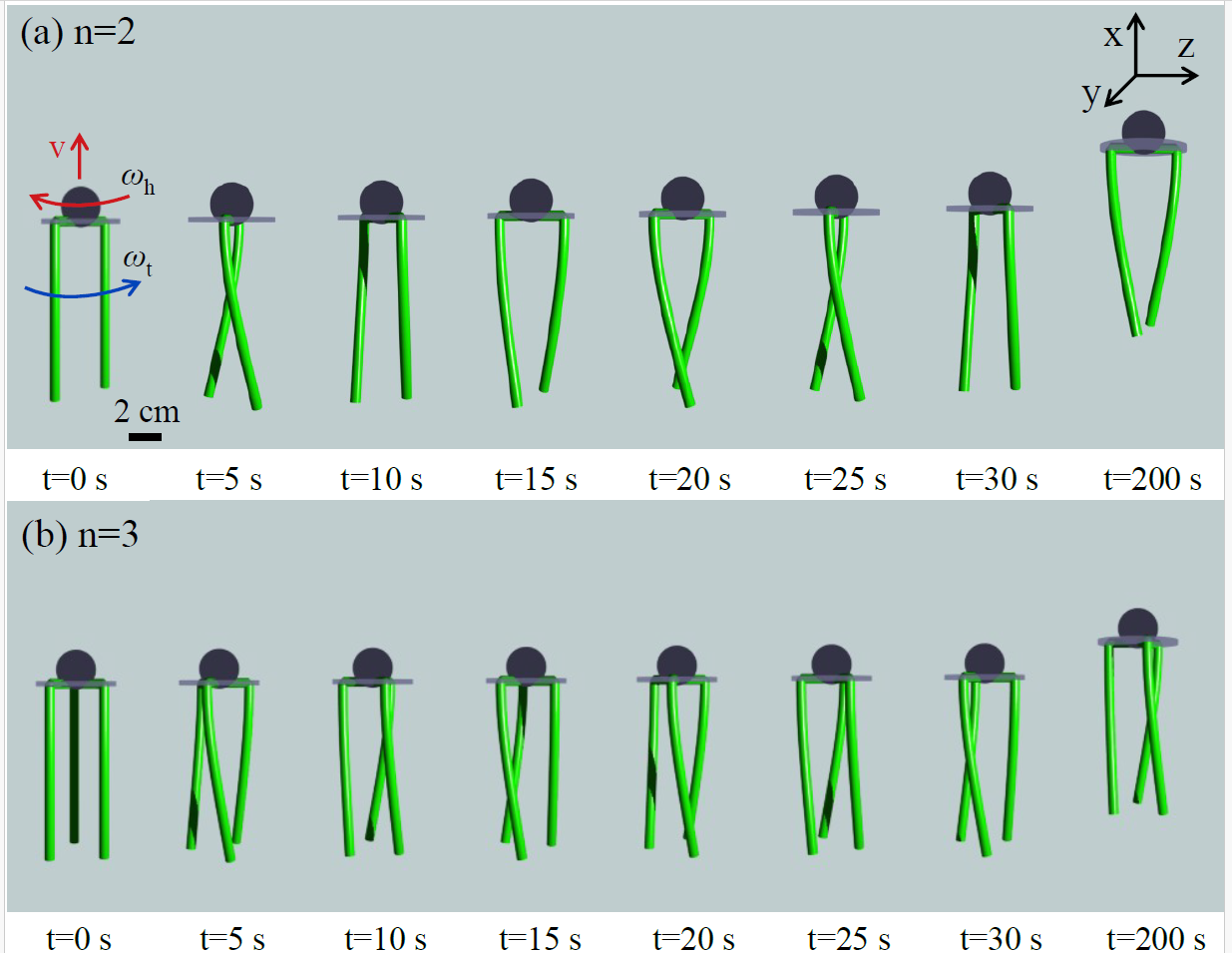
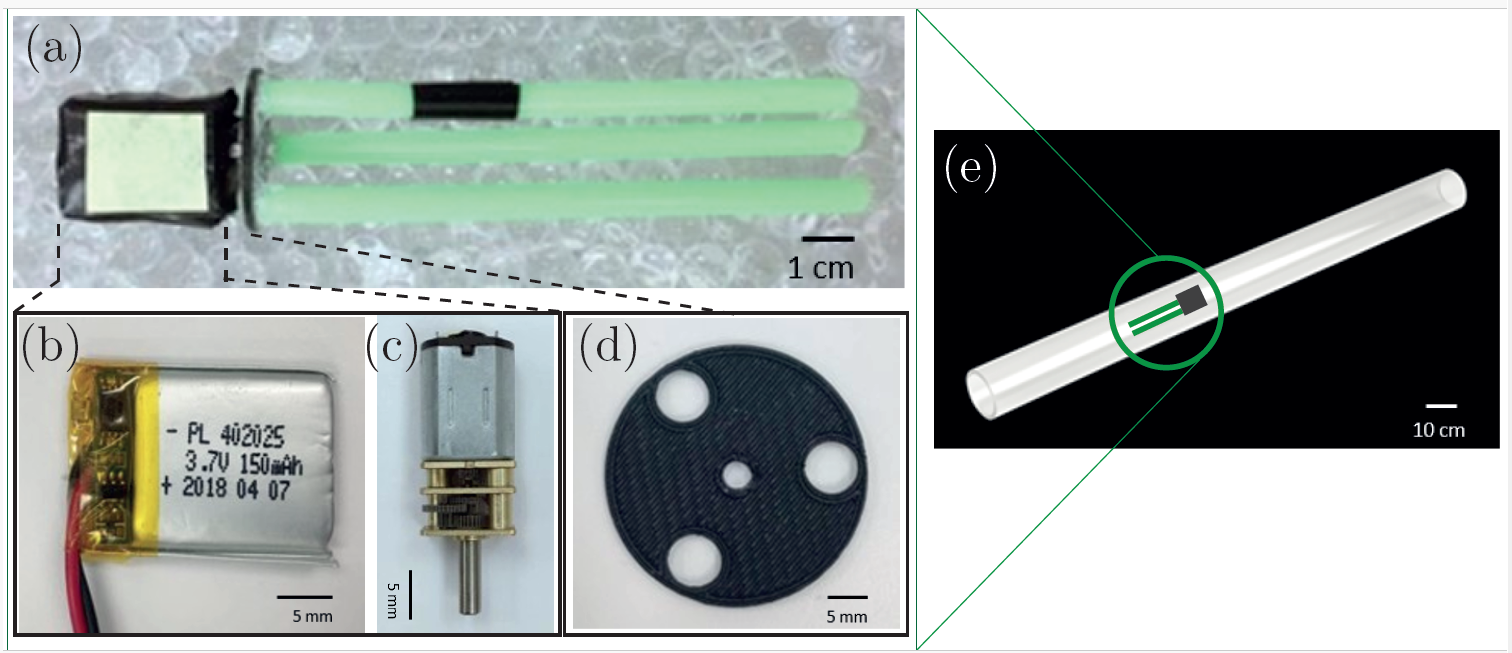
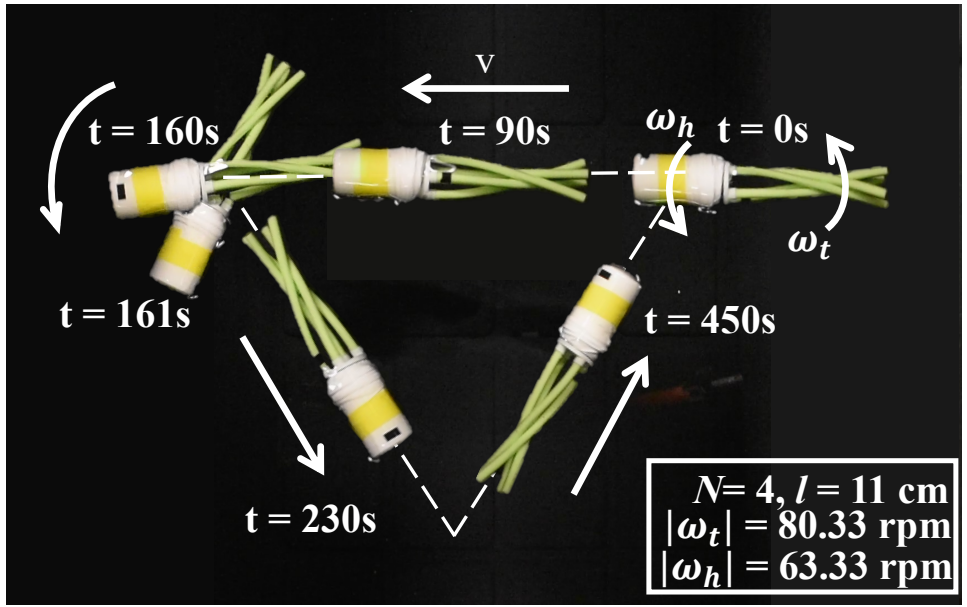
- Du, Y., Miller, A.#, Jawed, M. K., Simple Flagellated Soft Robot for Locomotion near Air-Liquid Interface, IEEE International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), Yale, CT, 2021 link
To be continued (Bacteria-inspired soft robots for autonomous navigation etc)
(# indicates students supervised or mentored by Yayun Du)